The Digital Competency Framework is developed as a foundation for training courses aimed at enhancing students' digital skills in the 21st century. The goal is to equip students with the necessary digital competencies to live, learn, work, and participate in social interactions proactively, positively, and safely in the digital environment. The framework is widely available to all organizations and training institutions as a reference for developing digital competency programs tailored to specific target groups.

Dr. Do Van Hung - Head of the research team - presented an overview of the digital competency framework.
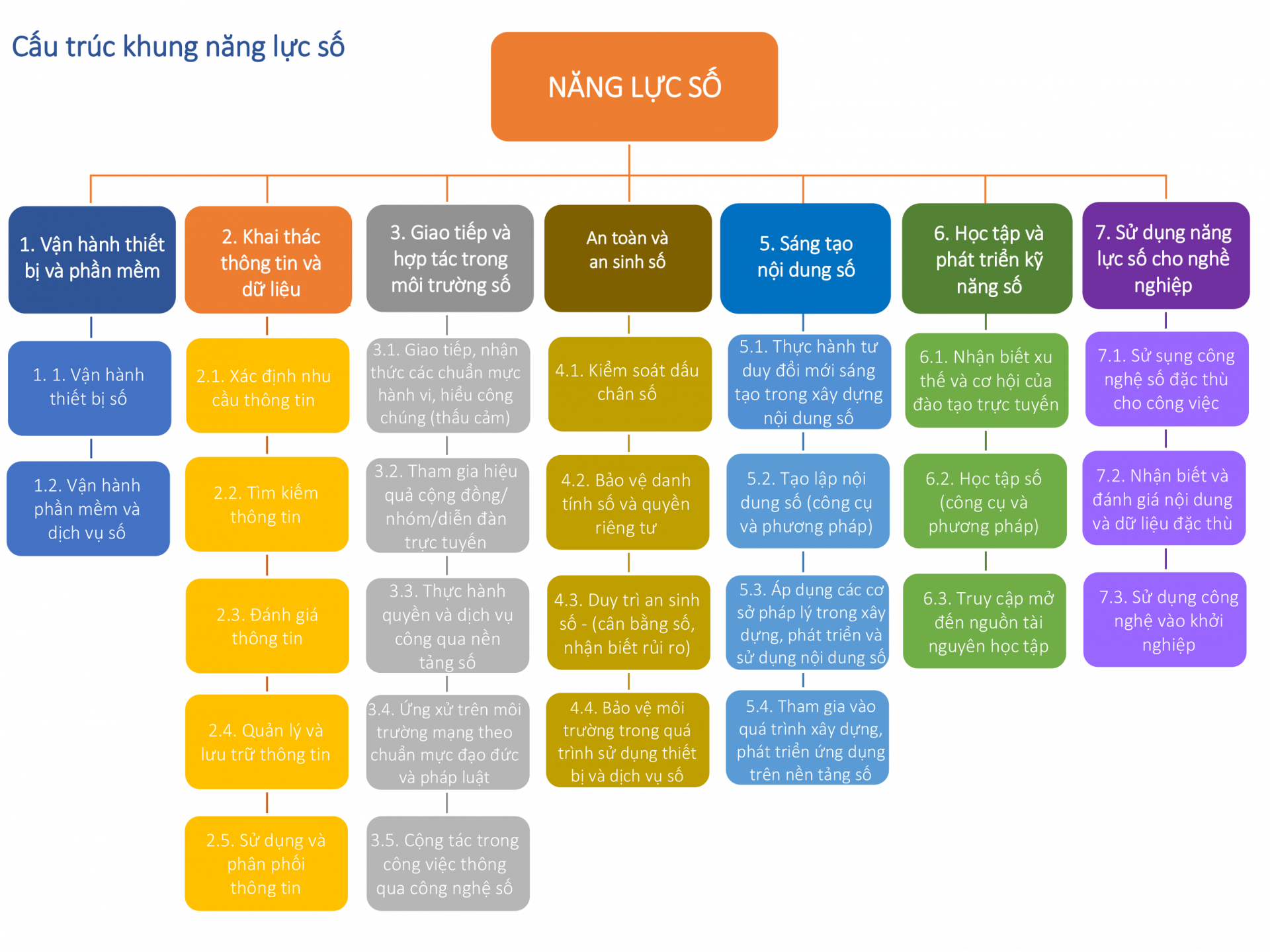
Based on a comparison of international competency frameworks, and referencing Facebook's approach in its We Think Digital courses, and applying the content of the Introduction to Digital Competency module, the research team proposes a digital competency framework model for students consisting of 7 competency groups with 26 standards.
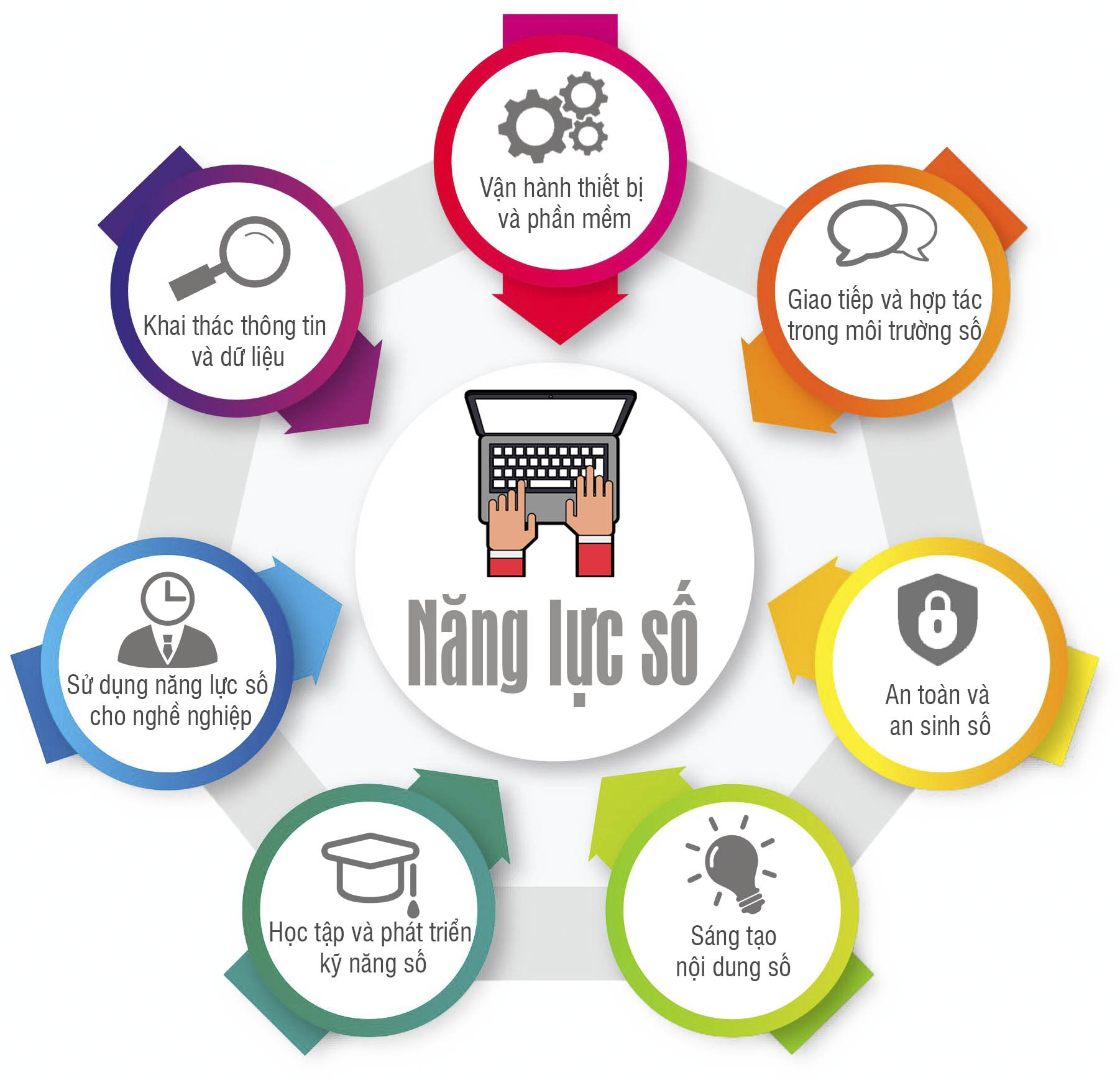
7 pillars of the Digital Competency Framework for Students
The specific competencies described within each of these major competency groups are also categorized and reorganized to place less emphasis on technical aspects of operations and more on applying technology to practice through attitudes, empathy, critical thinking, problem-solving, and innovation.
Brief description of the digital competency framework.
| No. | Competency group | Competency description |
|
|
Operating equipment and software | Recognize, select, and utilize hardware devices and software applications to identify and process digital data and information in problem-solving. |
|
|
Information and data mining
|
Identifying individual information needs; implementing strategies for finding, locating, and accessing information; evaluating information sources and their content; storing, managing, and organizing information; and using information ethically and legally. |
|
|
Communication and collaboration in the digital environment | Interact and communicate through digital technology and practice digital citizenship. Manage your own digital identity and reputation in the digital environment. Use digital tools and technologies to collaborate, co-design, and create information and knowledge resources. |
|
|
Digital safety and security
|
Protecting devices, content, personal data, and privacy in the digital environment. Protecting health and well-being. Awareness of the impact of digital technology on social well-being and social inclusion. Awareness of the impact of digital technology and its use on the environment. |
|
|
Digital content creation | Creating and editing digital content. Transforming and integrating digital information and content into existing knowledge bases. Understanding the licensing and copyright systems related to the digital content creation process. |
|
|
Learning and developing digital skills | Identify opportunities and challenges in the online learning environment. Understand individual needs and preferences as learners in a digital environment. Promote open access and information sharing. Recognize the importance of lifelong learning for personal development. |
|
|
Utilizing digital skills for your career. | Operating digital technologies in specific professional contexts. Understanding, analyzing, and evaluating data, information, and digital content specific to professional activities. Practicing innovation and entrepreneurship in a digital environment. |
Competency framework structure
This document is published as open access under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license. This license grants users the right to update and modify the content of this document to create derivative works, and to redistribute and commercialize them. A mandatory requirement for derivative works is to use the same license granted to the original work. See details at:https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/
Full text of the digital competency frameworkHERE
Author:USSH
Newer news
Older news