The VUCA world and the Fourth Industrial Revolution…
- In several recent forums, you've frequently mentioned the need to innovate human resource training to adapt to the very "new" and "different" labor market in the near future. You often refer to concepts such as the VUCA World and the Fourth Industrial Revolution (IR 4.0)... Could you please elaborate on these two concepts?The term "VUCA world" has existed for decades, formed from the first four letters of the terms Volatility, Uncertainty, Complexity, and Ambiguity. It was used by the US military during the Cold War and later by economists to describe unstable financial markets. Recently, many international higher education experts have used the term VUCA to describe the unpredictable changes in the labor market in the context of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industrial Revolution 4.0), which is having a significant impact on future careers.
The World Economic Forum (WEF) report “The Future of Jobs” published in 2016 estimated that: “For today’s generation of elementary school students, 65% will be doing jobs that do not yet exist.” According to WEF’s forecast, in the period 2015-2020, an average of 6 million jobs will be lost, while only about 2 million new jobs will be created, with a sharp decline in the public administration sector while new jobs will mainly be in high-tech and management fields.[1] In fact, the risk of labor market instability under the impact of modern technology has been warned about for decades. For example, exactly 20 years ago (1999), the US Department of Labor released an estimate of 65% as reported by the WEF. More recently, in 2017, Dell Technologies Corporation even provided a much higher estimate: in the next 10 years, approximately 85% of the workforce will be doing jobs that do not yet exist.
- So, many challenges and risks have arisen and are continuing to arise, requiring not only students but also lecturers and training institutions to innovate their training activities?Innovation is a mandatory attribute of any organization or society. Without innovation, there will be no development. Higher education is no exception; it needs to keep pace with the rapid development of technology and the labor market. I have previously mentioned some of the challenges facing universities today.
Firstly, the increasing demands of employers for qualities and skills in addition to the professional qualifications of students create pressure for innovation on universities in balancing the teaching of knowledge with the training of skills and the development of positive thinking in students. The volatility of future occupations means that university training activities face the risk of becoming outdated compared to the new workforce needs.
L
Signing ceremony of the cooperation and sponsorship agreement between the University of Social Sciences and Humanities and the Dao Minh Quang Foundation on developing a sustainable career and entrepreneurship project in Vietnam and continuing to provide scholarships for VNU-USSH students, November 2023.
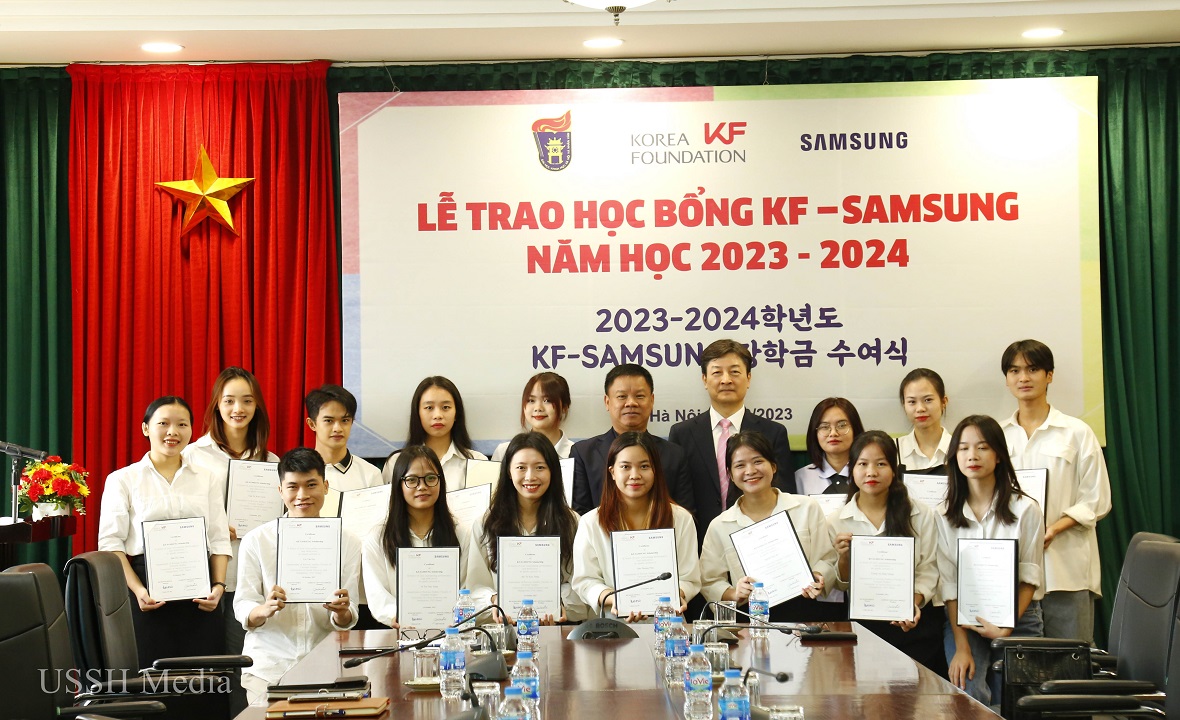
Students of the University of Social Sciences and Humanities receive recognition and support from numerous domestic and international scholarship funds.
Secondly, students have legitimate demands for a learning environment that extends beyond knowledge to include accompanying services: facilities, learning equipment, self-study spaces, cafeterias, internships/practical training (especially abroad), professional development clubs, cultural, sports, and arts activities, school-business connections, and startup support. There's a very existential example: the philosophy of "suffering to live happily" of 20th-century students is now considered "deviant" by the 10x generation, who see learning at school "not just as preparation for life, but as life itself"! Therefore, universities worldwide today are investing in improving facilities to attract students, encourage them to study and live on campus, thereby fostering their commitment to the school and preventing them from dropping out.
VNU-USSH is increasingly realizing the dreams of many generations of teachers and students for a spacious, modern, and humane learning and working environment.
Thirdly, there is the risk of losing market share in enrollment and training in traditional training fields, especially basic science fields which are becoming less attractive to students. In recent years, the total number of Vietnamese youth studying at universities in the country has steadily decreased, while the number of students studying abroad has increased sharply, not to mention the trend of "studying abroad locally" through distance or online training programs of foreign universities and international joint programs with domestic universities... According to the annual Open Doors report of the Institute of International Education (IIE), the number of Vietnamese students studying in the United States has continuously increased over the past 17 years, reaching 24,325 students in 2018, meaning that more than 800 million US dollars flowed from Vietnam to the United States last year,[2] not to mention the large number of Vietnamese students studying in other international education systems.

The University of Social Sciences and Humanities is hosting a training course on designing EMI (Employee-Integrated Learning) courses in English for university lecturers in Hanoi, with support from experts from the University of South Australia.
Fourth, the significant shift in employment patterns for graduates towards the non-public sector (private, international, non-governmental, startups, etc.) necessitates adjustments to training programs, classroom teaching time, investment in developing comprehensive skills, and fostering proactive attitudes and positive learning mindsets so that students can adapt to different work environments in the future. The World Education Summit (WISE) held in New York in September 2018 emphasized the importance of education in awareness and a "lifelong learning" mindset because knowledge acquired at university will quickly become outdated. Therefore, only with a perspective of continuous learning and a lifelong learning mindset can workers adapt to the changing landscape of future professions.
Fifthly, the slow pace of innovation in university management thinking has been warned about by education experts, especially in public universities. This risk leads to a failure to keep up with global university education trends, a backwardness in understanding, an inability to predict labor market trends, and even a failure to understand the changing needs of students themselves, resulting in university management failing to keep pace with student needs.
The Ministry's "sector" - the teacher's "profession" - the student's "vocation"...
So, it seems that one of the existing risks is the "outdated" and "static" nature of the current training structure in relation to the "new" and "dynamic" nature of future professions, sir?
The structure of training programs tends to change more slowly than the rapid changes in occupations and the labor market, especially in the context of the current Fourth Industrial Revolution. However, objectively speaking, the state's training program structure is not entirely "static" or "closed," but is constantly being supplemented by proposals from training institutions. Therefore, universities must both see their own interests and recognize their responsibility to develop new training programs based on future workforce needs, organize pilot training programs, and then propose to the Ministry of Education and Training to add them to the training program code. For example, more than two decades ago, the University of Social Sciences and Humanities pioneered the opening and pilot training of the Tourism Studies program, which has now been included in the state's official training program code.

S
Students majoring in Vietnamese Studies at the University of Social Sciences and Humanities. This is an interdisciplinary field of study that is increasingly attracting the attention of Vietnamese and foreign students.
- But besides the discussion about training programs, we also need to talk about the system of professional titles in society. How should these two aspects be considered in the context of new workforce training, sir?Previously, the concepts of "industry" and "profession" were discussed in a very close, organic relationship. According to traditional employment logic, graduates from a particular field of study tended to work in that field, related to the job codes and standards issued by the state. However, in recent years, the boundary between "industry" and "profession" has become increasingly blurred; the trend of studying one field and working in another is becoming more common. Ultimately, this is perfectly normal in any society if we look at labor and human resource trends in developed countries and the evolution of domestic policies, especially the policy of streamlining the workforce and restructuring the staff of officials, civil servants, and public employees in accordance with Resolutions 18 and 19 of the 6th Plenum of the 12th Central Committee.

International students pursuing bachelor's and master's degrees in Vietnamese Studies at the University of Social Sciences and Humanities have created a multicultural academic environment here.
Students from the Faculty of Vietnamese Studies and Vietnamese Language at the University of Social Sciences and Humanities, Vietnam National University, Hanoi, won first prize nationwide in the 2023 Vietnamese Public Speaking Competition for International Students (Photo: Tuoi Tre Newspaper)
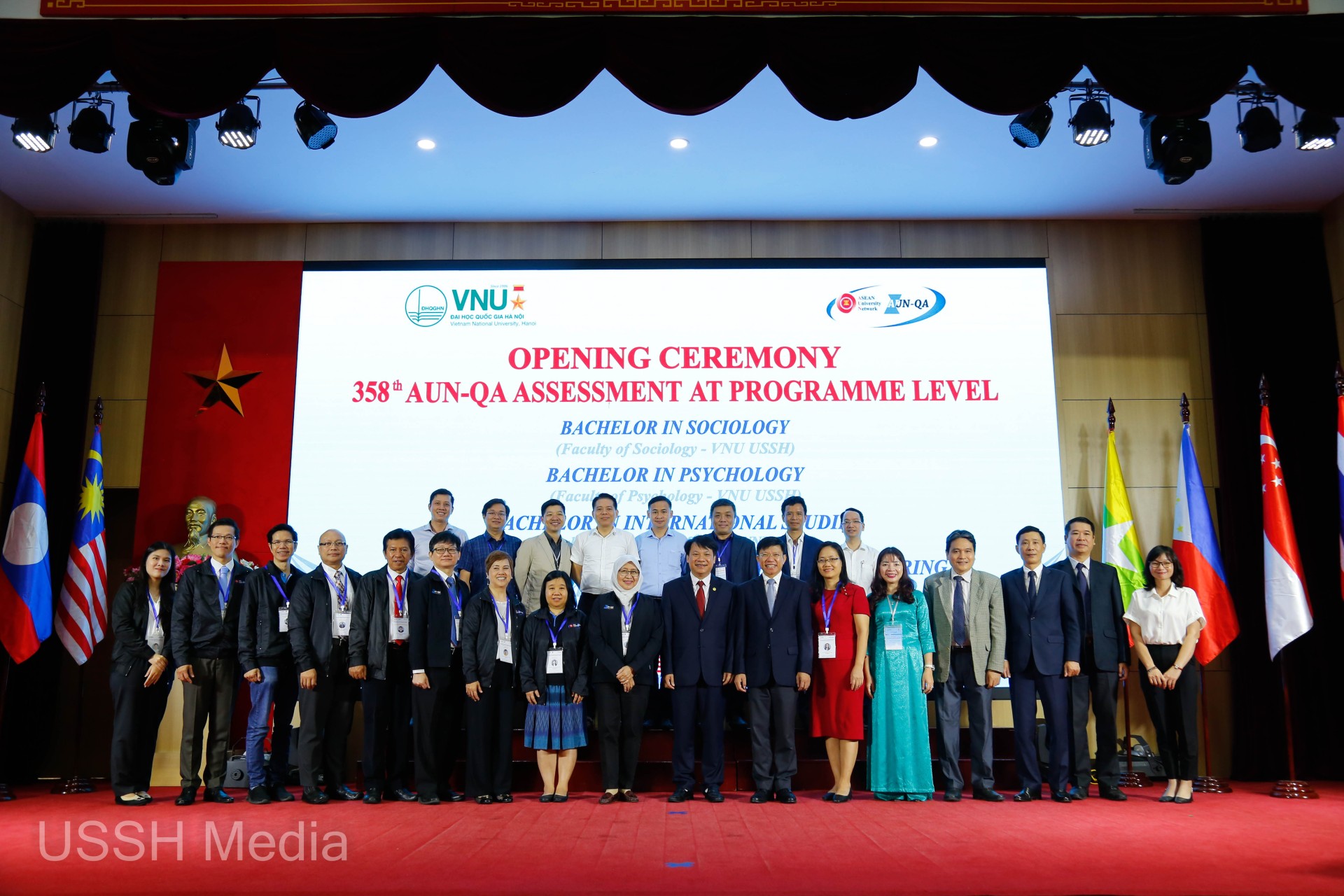
Accreditation of training programs according to international standards is a priority for the University of Social Sciences and Humanities, Vietnam National University, Hanoi, in order to improve and enhance the quality of its training programs. It is crucial that training institutions quickly and fully recognize this reality in order to adjust their training program structures accordingly. Besides opening new training programs to meet the workforce needs of Society 4.0, older programs that are no longer in high demand can be scaled down or considered for integration with related fields to form new ones. When there is no longer a societal need for human resources, a program will struggle to survive, except for fundamental sciences that are essential to any society, which the government will invest in maintaining. Globally, eliminating a training program that is no longer in demand is quite common, although it inevitably brings nostalgia and regret.

At the University of Social Sciences and Humanities, students are equipped with foundational knowledge in basic sciences to support their studies and research in their specialized fields; alongside critical thinking and the ability to adapt to the labor market. Every year, thousands of students participate in internships and practical training abroad as an important part of the university's curriculum.
Looking at the dynamics of the labor market in recent years and predicting labor trends over the next decade, the key concern now is how to harmonize three main elements: the "fields" set by the Ministry, the "professions" of the teachers, and the "careers" of the students. The State has been quite open regarding training program codes, and the labor market has been quite transparent about the trends guiding graduates to establish careers and start businesses. Therefore, lecturers and universities need to be proactive and decisive in bridging the gap between the two ends: students and the labor market. In other words, teachers must constantly innovate and create to both maintain their passion and chosen profession, while ensuring the formation of new training programs that meet the career needs of students in the digital workforce era.
Advantages of Vietnam National University, Hanoi: Multidisciplinary/Basic Science foundation - interdisciplinary/transdisciplinary trends - Innovative/Creative thinking.
So, in your opinion, what will be the main trend for the future of the education system?Many different viewpoints have been presented. Personally, I believe that interdisciplinary and cross-disciplinary approaches will be the fundamental trend in the context of a university ecosystem operating on the principles of connectivity and innovation.
For quite some time, Vietnamese universities have followed a narrow and specialized field orientation. Specialized training has certain advantages, but in the era of digital workforce with artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, interdisciplinary/cross-disciplinary training offers more prominent advantages. Education experts have recently been discussing a new workforce training model called "T-shaped People," based on a combination of the philosophy of knowing something about everything with the perspective of knowing everything about something (of the previous I-shaped People model). New work practices require future workers to possess broad knowledge and a wide range of problem-solving skills, rather than just specialized and narrow knowledge, which can be solved by artificial intelligence (AI). For example, in many countries today, single jobs such as hotel receptionists, tour guides, and sales staff have been completely replaced by robots. In the near future, more complex professions such as translation, legal consulting, and teaching may also be performed by machines with artificial intelligence. Therefore, the workforce for the Industry 4.0 labor market needs more than just single-specialized knowledge; learners need to be equipped with multidisciplinary, interdisciplinary knowledge, positive thinking, and comprehensive skills.

Hanoi University of Humanities students are healthy and active in arts, culture, and sports activities.
The curriculum at the University of Social Sciences and Humanities, Vietnam National University, Hanoi, emphasizes organizing internships and practical activities for students.
In particular, alongside scientific and technological knowledge (STEM), people are beginning to talk about the crucial role of philosophy, ethics and humanities, art... At the recent International Education Summit, the President of the Institute of International Education (IIE), Allan Goodman, argued that technologies capable of transforming society on a large scale will be those that require the strongest ethical foundation, and that judgments based on morality and ethics can be revolutionary in the 4.0 era.[3]
- What advantages would the University of Social Sciences and Humanities have if it implemented interdisciplinary/cross-disciplinary training and a spirit of innovation and creativity as a university, sir?The University of Social Sciences and Humanities in particular, and Vietnam National University, Hanoi in general, has a significant advantage in adapting to human resource training in the digital age because it is a leading multidisciplinary university in the country, harmonizing basic and applied sciences. In the social sciences and humanities, besides maintaining basic sciences – which are essential for any nation – the University is developing "hybrid" majors based on linking existing disciplines. For example, alongside International Studies and Anthropology, the University is developing a "International Development Studies" (IDS) major; and alongside the three existing majors – Sociology, Social Work, and Psychology – the University is researching the development of a hybrid major to serve the practical needs of Aging and Social Development…
Psychotherapy, in particular, requires interdisciplinary knowledge.